Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, could help protect your brain by supporting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) - a critical defense system that shields your brain from harmful substances. However, curcumin’s effectiveness is often limited by poor absorption and its difficulty crossing the BBB. Recent advancements in delivery methods, like nanoparticles and liposomal formulations, are solving this problem, making curcumin a more practical option for brain health.
Key Takeaways:
- Why BBB Health Matters: The BBB regulates what enters the brain, preventing toxins and pathogens from causing damage. A weakened BBB is linked to aging, cognitive decline, and neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- How Curcumin Helps: It strengthens the BBB by neutralizing free radicals, reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and preventing brain cell damage.
- Absorption Challenges: Over 90% of curcumin struggles to cross the BBB due to poor bioavailability.
- Solutions: Advanced delivery systems - like nanoparticles, liposomes, and self-microemulsifying drug systems - boost curcumin’s absorption by up to 55.4 times, enhancing its protective effects.
Quick Comparison of Delivery Methods:
| Delivery Method | Bioavailability Improvement | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piperine Complex | 2,000% increase | Simple, well-researched | Limited brain penetration |
| PLGA Nanoparticles | 15.6-fold increase | Stable, controlled release | Moderate encapsulation efficiency |
| PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles | 55.4-fold increase | Enhanced circulation | Complex manufacturing process |
| Liposomal Formulation | Moderate improvement | Biocompatible, less toxic | Lower encapsulation efficiency |
| SMEDDS | 1,213% increase | Exceptional absorption | Requires complex formulation |
Curcumin’s potential to protect the BBB is promising, especially with these delivery advancements. Whether you’re looking to maintain cognitive health or prevent neurodegeneration, curcumin combined with innovative formulations could be a valuable addition to your health toolkit.
The Blood-Brain Barrier and What Damages It
How the Blood-Brain Barrier Works
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) acts as a highly selective shield between the bloodstream and the brain, controlling what substances can pass through. It’s made up of four critical components: endothelial cells, pericytes, a basement membrane, and astrocyte end-feet. Together, these elements regulate the flow of substances to protect the brain.
In adults, the BBB spans an estimated surface area of 12 to 18 square meters (about 130 to 194 square feet) [5]. Pericytes, which are specialized cells, cover nearly the entire vascular system of the central nervous system [4]. The barrier is incredibly restrictive, allowing only small, hydrophobic, and non-polar molecules to pass through. In fact, it blocks over 98% of small-molecule drugs and larger therapeutic compounds [4]. However, essential molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and certain hormones can cross freely. Beyond filtering substances, the BBB also maintains the brain’s internal balance by regulating ion channels and transporters. Understanding its structure is key to exploring the factors that can weaken it.
What Weakens the Blood-Brain Barrier
Several factors can compromise the BBB's protective function. Oxidative stress is one of the most significant threats. Since the brain uses about 20% of the body’s oxygen supply [6], it’s especially vulnerable to damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS). When oxidative stress overwhelms the brain’s natural antioxidant defenses, it can harm the endothelial cells and disrupt the tight junctions that keep the barrier intact.
Chronic inflammation also plays a role in weakening the BBB. When proteins manage to enter the brain, they trigger microglial cells, which initiate an inflammatory response that can cause additional damage. Aging naturally reduces the BBB’s effectiveness, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s can speed up this decline, leaving the brain more exposed to harmful substances. These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of protecting the BBB.
Why BBB Health Matters
The BBB is essential for protecting the brain and ensuring proper neurological function. It acts as a frontline defense, keeping toxins, pathogens, and other harmful agents out while maintaining the brain’s delicate chemical environment. When the barrier is compromised, it can lead to a variety of neurological issues, including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and brain infections [7].
Even minor disruptions in the BBB can cause lasting damage, as they often lead to neuroinflammation and swelling [7]. New research suggests that a breakdown in the BBB could be an early warning sign of neurological diseases, emphasizing its role in preventing age-related cognitive decline and supporting long-term brain health [7]. Without a fully functioning BBB, the central nervous system becomes more vulnerable to toxins and pathogens, which can result in neuronal damage and degeneration [8]. Strengthening the BBB is critical, and boosting antioxidant defenses - such as through compounds like curcumin - may help counter the factors that damage it.
The power of Curcumin – introducing Longvida
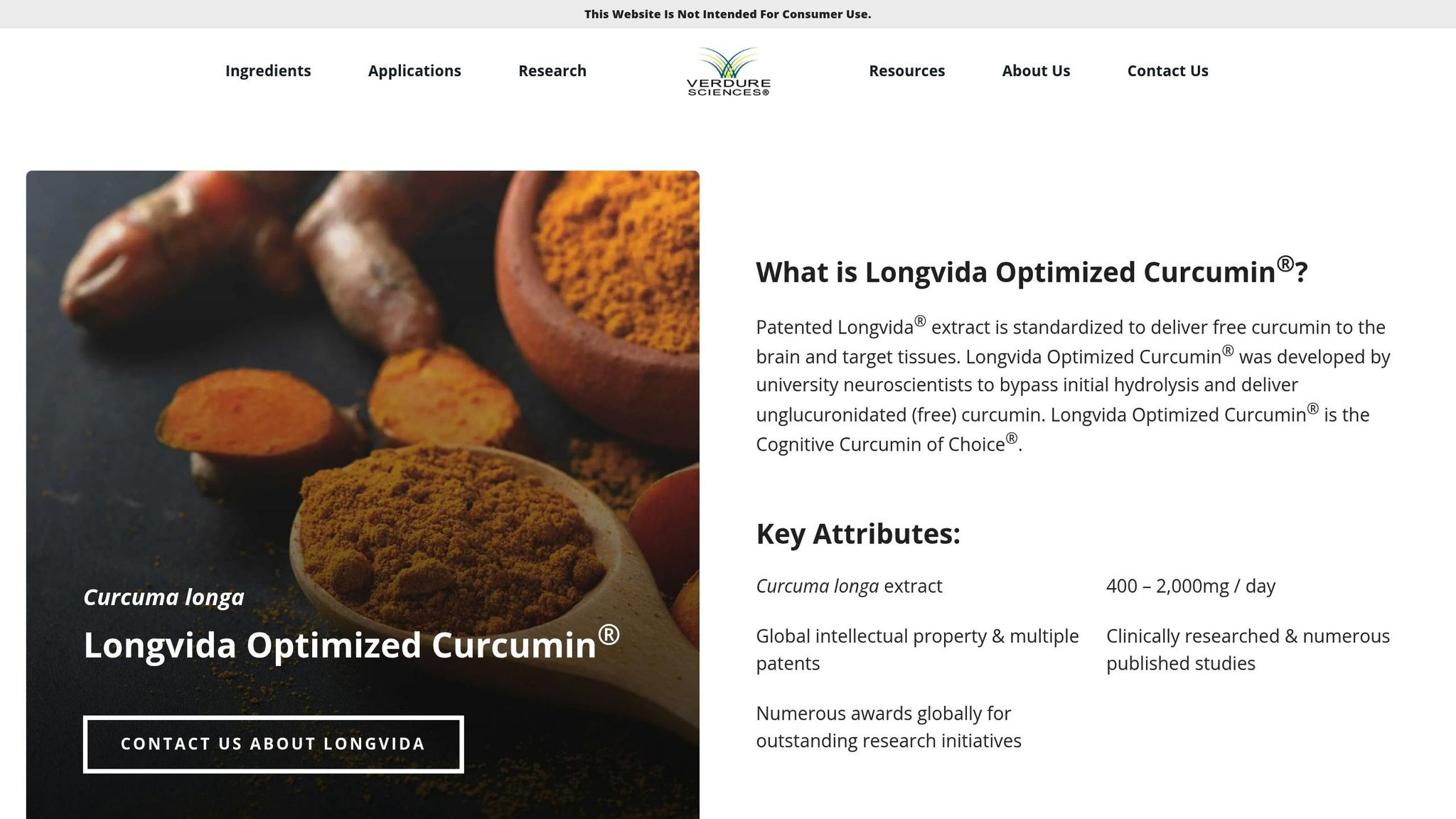
How Curcumin Protects the Blood-Brain Barrier
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays a crucial role in shielding the brain from harmful substances, but it's highly vulnerable to oxidative stress and inflammation. This is where curcumin steps in, offering several protective benefits that help maintain the barrier's integrity.
Antioxidant Protection
Curcumin acts as a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species like hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, and superoxide radicals that can damage endothelial cells within the barrier. It also boosts the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, and activates the Nrf2 signaling pathway. This pathway triggers the production of protective enzymes like NQO1, HO-1, and GST, further strengthening the barrier's defenses against oxidative damage [10].
Reducing Brain Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a major threat to the BBB, and curcumin tackles this issue by suppressing NF-κB, a key driver of inflammation. This action reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Preclinical studies highlight curcumin's ability to lower glial cell activation and decrease levels of inflammatory mediators, effectively countering neuroinflammation that compromises barrier integrity [11][12].
Improving Blood Vessel Function
The health of blood vessels directly impacts the BBB. Curcumin supports endothelial function by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, while also increasing nitric oxide bioavailability. Research involving middle-aged and older adults has shown that curcumin supplementation improves endothelial performance, which in turn benefits the BBB [13]. Additionally, curcumin activates the AMPK/UCP2 pathway, enhancing cerebrovascular function and creating a foundation for better brain protection [14].
Preventing Brain Cell Damage
Curcumin offers direct protection to brain cells by targeting harmful processes like amyloid‑β formation and tau protein hyperphosphorylation [9]. It strengthens the BBB by upregulating tight junction proteins and reducing factors that increase permeability. Furthermore, curcumin promotes the expression of aquaporin 4, which helps manage brain edema and maintain fluid balance [1]. Its ability to bind with metals adds another layer of protection, reducing metal-induced oxidative stress.
Removing Toxic Metals
Another way curcumin supports the BBB is by binding to toxic metals that can trigger free radical production. By mitigating metal-induced oxidative stress and inflammation, curcumin provides additional protection for the barrier [12].
Through these mechanisms, curcumin emerges as a valuable ally in preserving the brain's vital defenses.
sbb-itb-4f17e23
Solving Curcumin's Absorption Problems
Curcumin is known for its protective effects on the blood-brain barrier. However, its potential is often limited by poor absorption, which makes it difficult for the compound to reach therapeutic levels in the brain.
The main challenge lies in curcumin's low bioavailability. For starters, curcumin isn’t very water-soluble - its solubility at gastric pH is only 0.4 μg/mL [20]. On top of that, its chemical structure, particularly the hydroxyl groups, leads to rapid metabolism by kidney and liver enzymes [3]. When taken orally, about 90% of curcumin is excreted in feces, meaning very little actually enters the bloodstream [17]. Even when curcumin does make it into circulation, it faces another hurdle: the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The BBB’s tight junctions, active efflux transport proteins, and enzymes create a tough barrier to entry [15]. To address these challenges, researchers have developed innovative delivery systems to improve curcumin's absorption and effectiveness.
Better Ways to Deliver Curcumin
To tackle curcumin's absorption issues, scientists have designed advanced delivery systems that protect it from degradation, enhance solubility, and improve its ability to cross the BBB.
Nanoparticle encapsulation is one of the most promising strategies. Medical nanoparticles, typically smaller than 200 nanometers, can increase curcumin’s solubility and stability by shielding it from premature breakdown. Studies show that nanoparticle formulations can significantly extend curcumin’s retention in the brain. For instance, nanoparticulation increased curcumin retention in the cerebral cortex by 96% and in the hippocampus by 83% [21]. Research also highlights that curcumin nanosuspensions improved oral bioavailability by three- to four-fold in rats, and intravenous administration led to a 4.2-fold increase [17].
Liposomal formulations provide another effective method. These formulations enhance bioavailability and have shown promise in therapeutic applications. Although the encapsulation efficiency for curcumin in liposomes is around 33% [18], studies suggest liposomal curcumin outperforms curcumin solutions in preserving pancreatic function and reducing inflammation [19].
PLGA-based nanoparticles are also gaining attention. In one study, curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles achieved a particle size of 163 nanometers and an entrapment efficiency of 46.9% [21]. These nanoparticles boosted curcumin bioavailability by 15.6-fold, while PLGA-PEG nanoparticles achieved an impressive 55.4-fold increase compared to a simple curcumin suspension [21].
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) have delivered notable results as well. One formulation improved oral bioavailability by a staggering 1,213% compared to a curcumin suspension [17].
Researchers are also exploring advanced methods for direct brain delivery. For instance, low-intensity focused ultrasound combined with curcumin-loaded lipid-PLGA nanobubbles can temporarily open the BBB, allowing curcumin to penetrate deep into brain tissue [23]. Additionally, modifying the surface of liposomes with sialic acid and wheat germ agglutinin may further enhance their ability to cross the BBB [22].
Comparing Delivery Methods
Here’s a quick summary of the key delivery methods and their benefits:
| Delivery Method | Bioavailability Improvement | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piperine Complex | 2,000% increase [16] | Simple and well-researched | Limited brain penetration |
| PLGA Nanoparticles | 15.6-fold increase [21] | Stable and offers controlled release | Moderate encapsulation efficiency |
| PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles | 55.4-fold increase [21] | Enhanced circulation and bioavailability | Complex manufacturing process |
| Liposomal Formulation | Improvement [19] | Biocompatible and less toxic | Lower encapsulation efficiency |
| SMEDDS | 1,213% increase [17] | Exceptional absorption enhancement | Requires complex formulation |
| Nanosuspensions | 3–4 fold increase (oral) [17] | Scalable production and improved solubility | Requires stabilizers |
The development of curcumin formulations has evolved across three generations. First-generation approaches, like curcumin-piperine complexes, improve absorption by slowing metabolism. Second-generation solutions, including Theracurmin, Meriva, and CurcuWIN, use emulsifiers and nanoparticles to boost solubility. Third-generation formulations, such as Longvida and CurQfen, have tackled bioavailability without relying on artificial emulsifiers, leading to better membrane permeability and cellular uptake [24].
These advancements are making it easier for curcumin to deliver its protective benefits to brain tissue, offering new hope for harnessing its full potential.
Research Evidence and Clinical Studies
Research shows that curcumin plays a role in strengthening the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and improving neurological outcomes, particularly when delivered through advanced formulations. However, turning these laboratory findings into practical clinical applications remains a challenge.
Lab and Early Human Studies
Curcumin's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties are crucial for its ability to protect the BBB, as confirmed by multiple studies.
For example, a study from the Chinese University of Hong Kong demonstrated that nanocurcumin improved memory in Tg2576 mice and increased brain curcumin levels sixfold [27]. Similarly, research in Neurobiology of Aging found that a curcumin derivative, Derivative 27, enhanced spatial short-term memory and reduced inflammation in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice [28].
At Jazan University in Saudi Arabia, a combination of turmeric extract and essential oil (TE+EO) significantly boosted free curcumin concentrations in the brain - up to 13.7 times more than turmeric extract alone. This formulation reversed aluminum-induced memory impairment by nearly 40% and improved anxiety-related behaviors by 67.1% [2].
Innovative delivery methods have also shown promise. Curcumin-loaded exosomes successfully crossed the BBB to protect mice from septic shock and treat gliomas [25][26]. Dendrosomal curcumin nanoparticles were found to promote remyelination and enhance oligodendrogenesis in demyelination models [26].
A review of 11 clinical studies on curcumin nanoformulations highlighted significant improvements in bioavailability, with increases ranging from 9- to 185-fold [25]. Advanced formulations achieved over 100-fold increases in free curcumin levels in plasma, showing improved cellular uptake and BBB permeability [25].
These findings underscore curcumin's potential but also highlight the need for more clinical validation.
What Research Is Still Needed
While laboratory results are encouraging, translating them into clinical practice presents several hurdles.
One major challenge is curcumin's poor water solubility, which limits its effectiveness [29]. Determining the right dosages and administration schedules is also critical, as current studies lack clear guidelines for therapeutic use while ensuring safety. Long-term studies are particularly important, as sustained treatment may be necessary to protect the BBB over time [30].
Understanding curcumin's molecular mechanisms could help identify which patient groups would benefit most and how it might be combined with other therapies [29]. Additionally, most human studies to date have been small and short-term. Larger, long-term trials are needed to evaluate its effectiveness across diverse populations [29].
With the variety of curcumin formulations available, comparative studies are essential to identify the safest, most effective, and practical options.
MASI Longevity Science's Commitment to Brain Health
At MASI Longevity Science, we understand that protecting brain health demands rigorous research and high-quality formulations. Our supplements for brain and vascular health reflect this commitment, translating scientific advancements into practical solutions for our global community of over 352,000 members.
Our products are manufactured in Germany using pharmaceutical-grade raw materials and undergo independent safety and efficacy testing in Switzerland. This careful approach is especially vital for compounds like curcumin, where formulation quality directly impacts bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness.
While we stay informed about emerging research on curcumin and BBB protection, our current focus is on our proven anti-aging supplements: NMN, Resveratrol, Fisetin, and Spermidine. These products target the key drivers of aging and support cellular renewal, brain health, and cardiovascular function, with backing from research conducted by leading institutions like Harvard and the Mayo Clinic.
Beyond individual products, we are dedicated to advancing the science of longevity. As research on curcumin evolves, we integrate new findings to continually improve our formulations. Our mission is to provide supplements that genuinely enhance your health and longevity journey, rooted in the most reliable scientific evidence available.
Conclusion
Curcumin plays a key role in protecting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by neutralizing free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, and shifting microglia from a pro-inflammatory (M1) state to an anti-inflammatory (M2) state. This shift helps lower levels of cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β, as detailed earlier.
Its benefits don’t stop at inflammation control. Curcumin also supports brain health by reducing neurotoxicity, aiding tissue repair, and binding to toxic metals like iron and copper, which can otherwise trigger harmful reactions. These combined effects make curcumin especially helpful during ischemic events or in neurodegenerative conditions, where the BBB faces its toughest challenges.
However, curcumin's limited ability to cross the BBB has led to innovations in delivery methods. Advanced formulations, such as CurQfen®, have shown dramatically improved bioavailability and BBB penetration, making curcumin a more practical therapeutic option. These improved formulations not only address absorption issues but also contribute to a broader approach for sustained cognitive health.
When combined with other well-researched supplements, curcumin’s protective effects on the BBB may help preserve cognitive function and slow neurodegeneration. This aligns directly with MASI Longevity Science's mission to integrate scientific advancements into meaningful solutions for our community.
At MASI Longevity Science, we pair rigorous research with uncompromising quality standards. While we continue to track developments in curcumin research, our focus remains on our proven anti-aging supplements, including NMN, Resveratrol, Fisetin, and Spermidine. Manufactured in Germany and tested in Switzerland, our products reflect our dedication to providing over 352,000 community members with reliable, science-driven solutions for brain and vascular health as part of their longevity journey.
FAQs
How do advanced formulations like nanoparticles and liposomes help curcumin pass through the blood-brain barrier?
Advanced techniques like nanoparticles and liposomes are making it easier for curcumin to cross the blood-brain barrier, overcoming challenges like its low solubility and limited bioavailability. These methods shrink curcumin molecules, enhance their fat solubility, and improve their interaction with cell membranes, allowing for smoother transport into the brain.
By boosting curcumin's stability and ability to penetrate, these formulations help it reach specific brain tissues more efficiently. This not only supports the integrity of the blood-brain barrier but also promotes overall brain health.
How can curcumin help protect the blood-brain barrier, and what neurological conditions might benefit from this effect?
Curcumin has been found to help maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by tackling inflammation, reducing oxidative stress, and aiding cellular repair. These properties make it a promising candidate for addressing neurological conditions tied to BBB dysfunction.
Here are some examples where curcumin may offer benefits:
- Alzheimer's disease: It may help by reducing amyloid plaque buildup and curbing inflammation.
- Stroke and traumatic brain injury: Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects could support recovery.
- Neurodegenerative disorders: Conditions like Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease might benefit from curcumin’s ability to reduce neuronal damage.
Ongoing research continues to shed light on curcumin’s potential to promote brain health and provide protection against various neurological issues.
What are the potential risks or side effects of using advanced delivery systems to improve curcumin's absorption?
Curcumin's advanced delivery systems aim to improve its absorption and are generally considered safe when used correctly. However, consuming curcumin in very high doses can lead to potential issues. These might include liver toxicity, mild digestive upset, or irritation. Some people might also experience cold-like symptoms or have trouble digesting larger amounts of curcumin.
To stay on the safe side, stick to recommended dosages and seek advice from a healthcare provider before adding curcumin supplements to your routine - especially if you have existing health conditions or are on medication.




